Processed Foods: Your Complete Guide
 Processed foods dominate modern diets, but understanding what they are and their impact on your health is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of processed foods, exploring their definition, levels of processing, health implications, and how to make informed choices.
Processed foods dominate modern diets, but understanding what they are and their impact on your health is crucial. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of processed foods, exploring their definition, levels of processing, health implications, and how to make informed choices.
What are Processed Foods?
Simply put, processed foods are any foods that have been altered from their natural state. This alteration can range from minimal changes like washing and packaging to significant transformations involving multiple ingredients and industrial processes. While some processing is necessary for food preservation and safety, excessive processing can strip foods of their nutritional value and add unhealthy ingredients.
Levels of Food Processing
Not all processed foods are created equal. Understanding the different levels of processing helps you differentiate between minimally processed foods that can be part of a healthy diet and ultra-processed foods that should be limited. The NOVA food classification system, developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo, is a widely used framework for categorizing foods based on the extent and purpose of processing.
1. Unprocessed or Minimally Processed Foods
These foods are in their natural state or have undergone minimal alterations. Examples include:* Fruits and vegetables: Fresh, dried, frozen, or chopped* Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, oats* Legumes: Beans, lentils* Meat and fish: Fresh or frozen cuts* Milk and eggs: Pasteurized milk, eggs* Nuts and seeds: Unsalted and unroasted nuts and seedsThese foods are essentially whole foods that have been cleaned, packaged, or minimally processed to make them easier to store and consume. They retain most of their original nutrients and are a cornerstone of a healthy diet.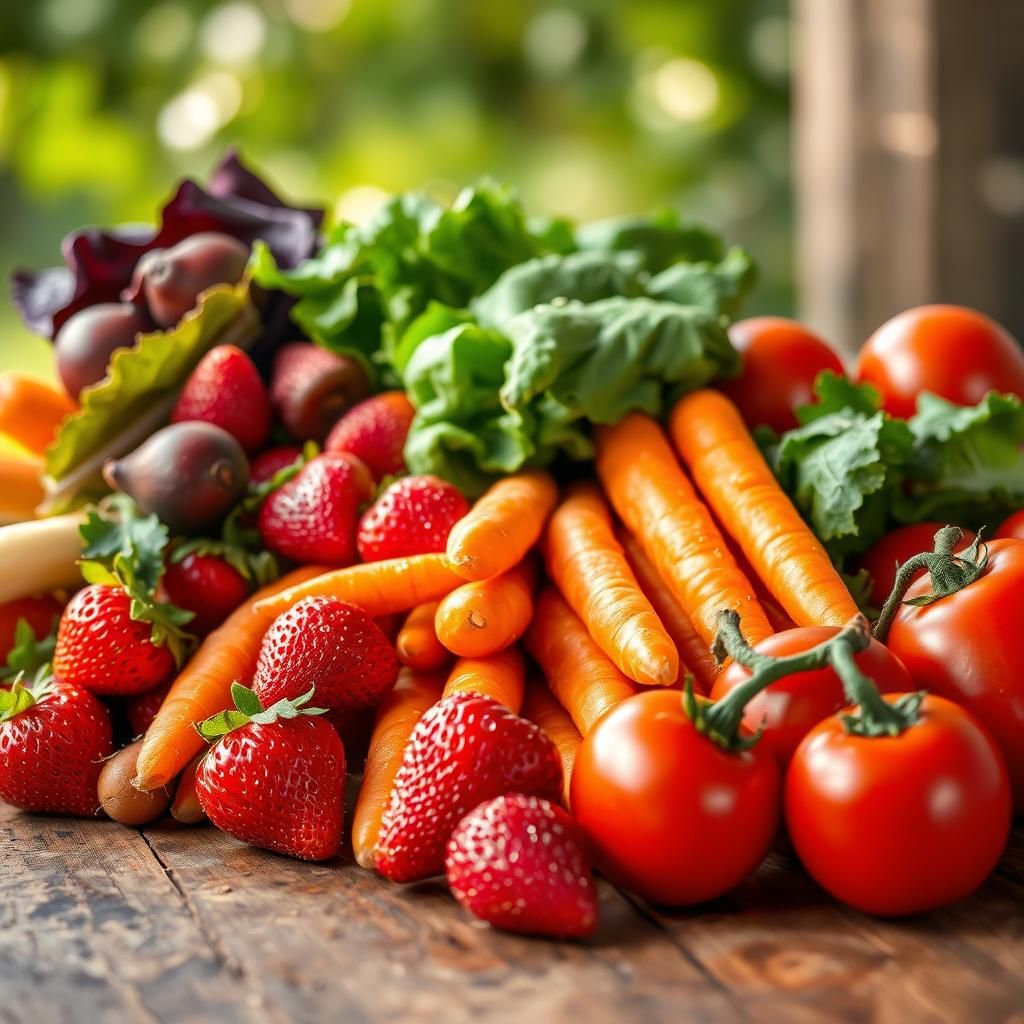
2. Processed Culinary Ingredients
These are substances extracted from unprocessed foods or nature and used in the preparation and cooking of food. Examples include:* Oils: Vegetable oils, olive oil* Fats: Butter, lard* Salt: Table salt, sea salt* Sugar: White sugar, brown sugarThese ingredients are essential for cooking and flavoring food, but they should be used in moderation.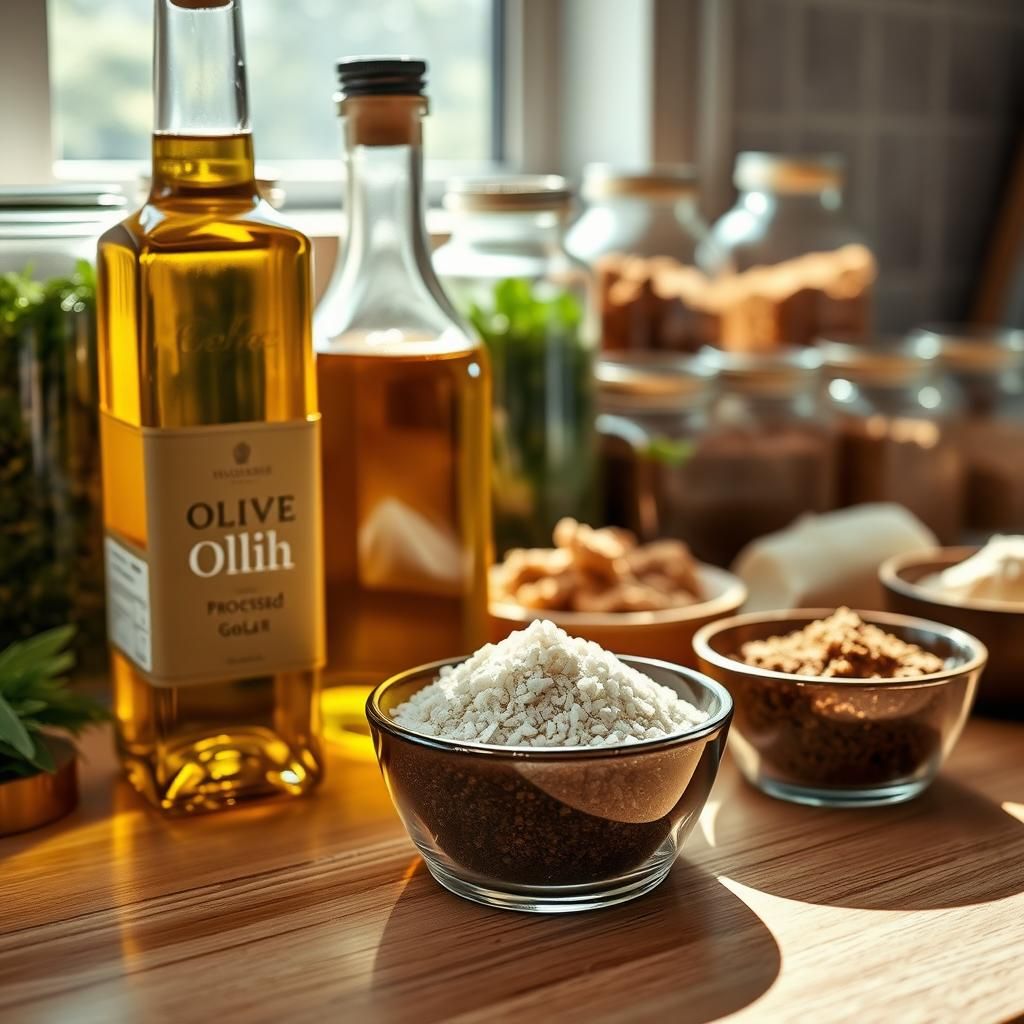
3. Processed Foods
These are foods made by adding ingredients like salt, sugar, oil, or other culinary ingredients to minimally processed foods. The purpose of processing at this level is to preserve the food or to change its sensory qualities. Examples include:* Canned fruits and vegetables: Fruits canned in syrup, vegetables canned in brine* Canned fish: Tuna in oil, sardines* Cheeses: Simple cheeses like mozzarella or cheddar* Bread: Freshly baked bread with limited ingredients* Smoked meats: Traditionally smoked meatsThese foods are often shelf-stable and can be a convenient option. However, it’s important to check the ingredient list and nutritional information to avoid excessive salt, sugar, or unhealthy fats.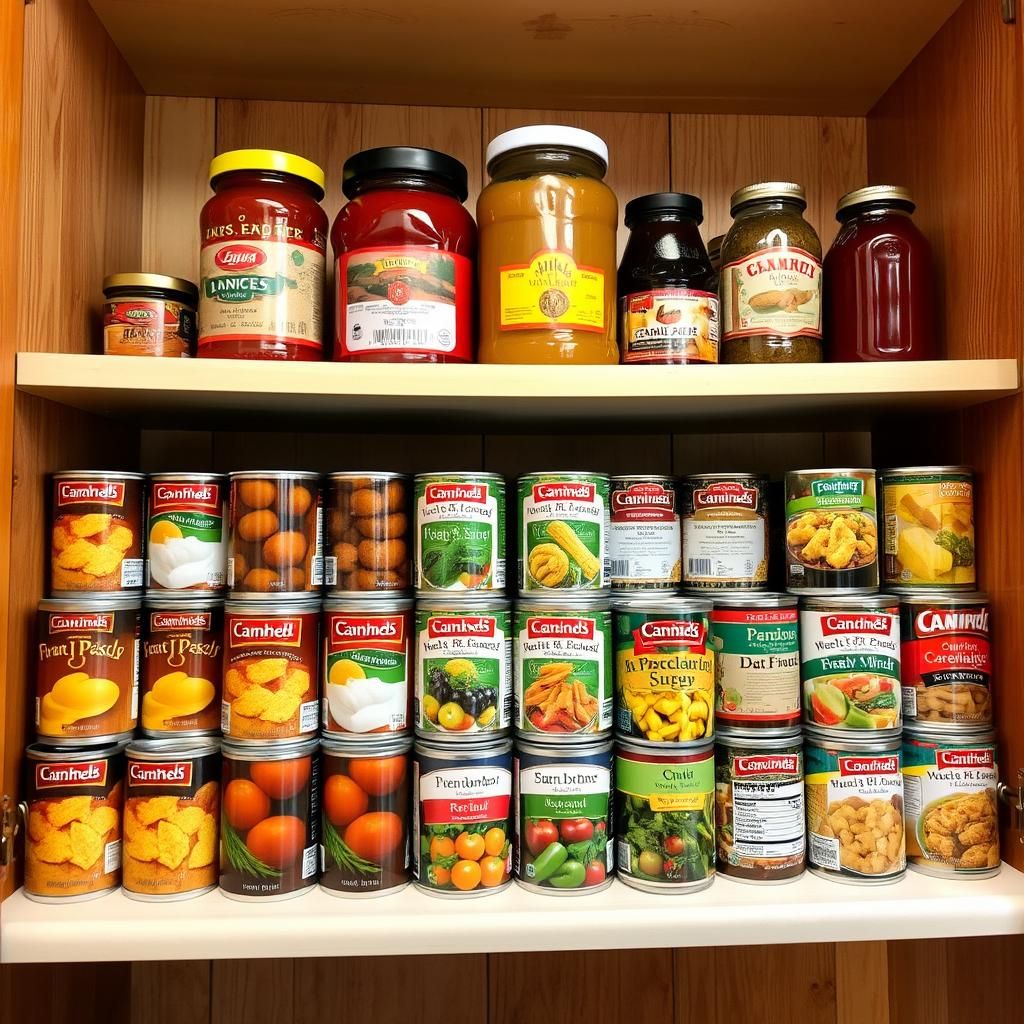
4. Ultra-Processed Foods
Ultra-processed foods are industrial formulations made entirely or mostly from substances extracted from foods (oils, fats, sugars, starch, and proteins), derived from food constituents (hydrogenated fats and modified starch), or synthesized in laboratories (flavor enhancers, colors, and other cosmetic additives). They typically contain little or no whole foods. Examples include:* Soft drinks: Sodas, sweetened beverages* Packaged snacks: Chips, cookies, crackers* Processed meats: Sausages, hot dogs, deli meats* Instant noodles and soups: Pre-packaged meals* Breakfast cereals: Sugary cereals* Frozen meals: Ready-to-eat mealsThese foods are often high in calories, sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats, and low in essential nutrients. Regular consumption of ultra-processed foods is linked to various health problems.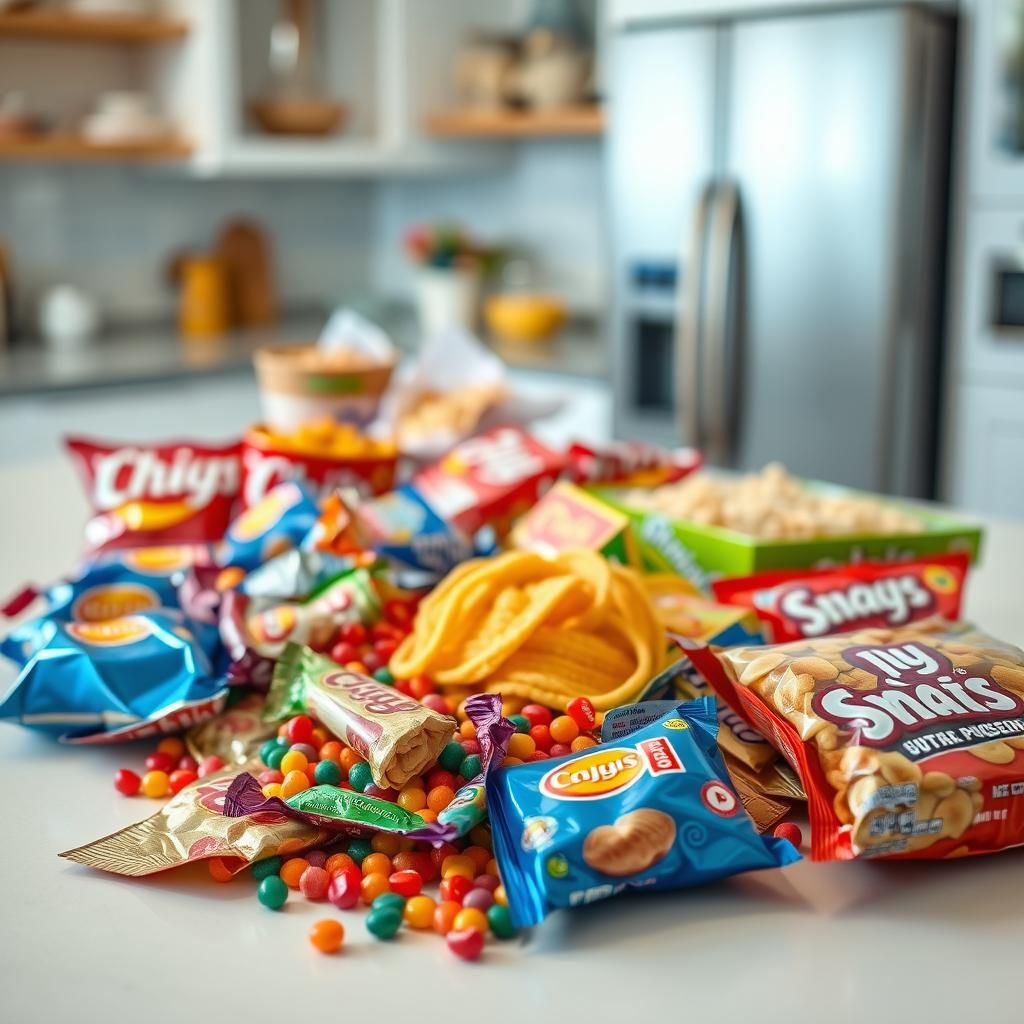
The Health Implications of Processed Foods
The impact of processed foods on health is a significant concern. While minimally processed foods can be part of a balanced diet, excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods is associated with a range of negative health outcomes.
1. Increased Risk of Obesity
Ultra-processed foods are often calorie-dense and low in fiber, leading to overconsumption and weight gain. Studies have shown a strong correlation between the intake of ultra-processed foods and obesity.* **Example:** A study published in the *British Medical Journal* found that a diet high in ultra-processed foods led to increased calorie intake and weight gain compared to a diet of minimally processed foods. Participants on the ultra-processed diet consumed an average of 500 more calories per day and gained weight during the study period.
2. Higher Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
The high sugar and refined carbohydrate content of many processed foods can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.* **Example:** Research published in *JAMA Internal Medicine* showed that a higher consumption of ultra-processed foods was associated with a significantly increased risk of type 2 diabetes. The study followed over 100,000 adults for several years and found a clear link between ultra-processed food intake and diabetes development.
3. Increased Risk of Heart Disease
Processed foods often contain high levels of saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars, all of which can contribute to heart disease.* **Example:** A study in the *American Journal of Clinical Nutrition* found that higher consumption of processed meats, such as bacon and sausages, was associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The study highlighted the detrimental effects of saturated fat and sodium found in these products.
4. Increased Risk of Certain Cancers
Some studies suggest a link between high consumption of ultra-processed foods and an increased risk of certain cancers, particularly those of the digestive system.* **Example:** Research published in *The BMJ* found that a 10% increase in the proportion of ultra-processed foods in the diet was associated with a significantly higher risk of overall cancer and breast cancer specifically.
5. Nutrient Deficiencies
Ultra-processed foods are often low in essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Relying heavily on these foods can lead to nutrient deficiencies and compromise overall health.* **Example:** Many processed snacks and meals lack sufficient fiber, which is crucial for digestive health and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. This can lead to constipation, increased risk of colon cancer, and poor blood sugar control.
6. Digestive Issues
The artificial additives and preservatives in processed foods can disrupt the gut microbiome and contribute to digestive issues like bloating, gas, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).* **Example:** Artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose, commonly found in diet sodas and sugar-free snacks, have been shown to alter the gut microbiome and potentially lead to digestive discomfort in some individuals.
How to Identify Processed Foods
Reading food labels carefully is essential for identifying processed foods and making informed choices. Here are some tips:
1. Check the Ingredient List
* Long ingredient list: A long list of ingredients, especially if many of them are unfamiliar or unpronounceable, is a sign of a highly processed food.* Added sugars: Look for added sugars like high fructose corn syrup, sucrose, glucose, and dextrose. These ingredients contribute to empty calories and can negatively impact health.* Unhealthy fats: Be wary of saturated and trans fats, often listed as hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils.* Artificial additives: Watch out for artificial colors, flavors, and preservatives. While some additives are harmless, others can cause adverse reactions in sensitive individuals.
2. Review the Nutrition Facts Label
* High in sodium: Processed foods are often high in sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure.* High in saturated and trans fats: These fats can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease.* Low in fiber: Fiber is important for digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. Choose foods with at least a few grams of fiber per serving.* High in added sugars: Added sugars contribute to empty calories and can increase the risk of weight gain and type 2 diabetes.
3. Be Wary of Marketing Claims
* “Natural”: The term “natural” is often used loosely and doesn’t necessarily mean that a food is healthy or minimally processed.* “Healthy”: The term “healthy” can be misleading, as some foods marketed as healthy may still contain high levels of sugar, salt, or unhealthy fats.* “Low-fat” or “fat-free”: These products often contain added sugars or artificial sweeteners to compensate for the lack of fat.
Making Informed Choices: Reducing Processed Foods in Your Diet
Reducing your intake of ultra-processed foods can have significant benefits for your health. Here are some practical tips for making healthier choices:
1. Cook More at Home
Preparing meals at home gives you control over the ingredients and allows you to use fresh, whole foods.* Tip: Plan your meals in advance and create a shopping list to avoid impulse purchases of processed foods.
2. Focus on Whole Foods
Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are packed with nutrients and fiber and are naturally low in added sugars, salt, and unhealthy fats.* Tip: Fill half of your plate with fruits and vegetables at each meal.
3. Read Labels Carefully
Take the time to read food labels and compare products. Choose options with shorter ingredient lists, lower levels of added sugars and sodium, and higher levels of fiber.* Tip: Become familiar with common food additives and their potential health effects.
4. Choose Minimally Processed Options
When buying processed foods, opt for minimally processed options like frozen fruits and vegetables, canned beans, and whole-grain bread.* Tip: Look for products with no added sugar, salt, or artificial additives.
5. Limit Sugar-Sweetened Beverages
Replace sodas, juices, and other sugary drinks with water, unsweetened tea, or sparkling water with a splash of fruit juice.* Tip: Keep a water bottle with you and sip on it throughout the day.
6. Snack Smart
Avoid processed snacks like chips, cookies, and candy. Instead, choose healthy snacks like fruits, vegetables with hummus, nuts, or yogurt.* Tip: Prepare a batch of healthy snacks at the beginning of the week to have on hand when hunger strikes.
7. Make Gradual Changes
Don’t try to eliminate all processed foods from your diet overnight. Start by making small, gradual changes, such as swapping sugary cereal for oatmeal or replacing processed snacks with fruits and vegetables.* Tip: Focus on adding more whole foods to your diet rather than simply restricting processed foods.
8. Be Aware of Emotional Eating
Pay attention to your eating habits and identify triggers for emotional eating. Find healthy ways to cope with stress and emotions, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones.* Tip: Keep a food diary to track your eating habits and identify patterns.
9. Experiment with Recipes
Explore new recipes that use whole, unprocessed ingredients. There are countless resources available online and in cookbooks to help you create delicious and healthy meals.* Tip: Start with simple recipes that require only a few ingredients and gradually work your way up to more complex dishes.
10. Educate Yourself
Stay informed about the latest research on processed foods and their impact on health. The more you know, the better equipped you’ll be to make informed choices.* Tip: Follow reputable health organizations and nutrition experts for evidence-based information.
A Delicious and Healthy Home-Cooked Meal
List of Commonly Processed Foods and Healthier Alternatives
To further guide your choices, here’s a list of common processed foods and healthier alternatives:| Processed Food | Healthier Alternative || ——————— | ——————————— || White Bread | Whole-Grain Bread || Sugary Cereal | Oatmeal with Fruit and Nuts || Processed Meats | Lean Poultry or Fish || Packaged Snacks | Fruits, Vegetables, Nuts, Seeds || Soda | Water, Unsweetened Tea, Sparkling Water || Frozen Meals | Homemade Meals with Whole Foods || Instant Noodles | Whole-Grain Pasta with Vegetables || Canned Soup | Homemade Soup with Fresh Ingredients || Salad Dressings | Olive Oil and Vinegar || Fruit Juice | Whole Fruit || Yogurt (Sugary) | Plain Yogurt with Fruit || Coffee Creamer | Milk or Almond Milk || Microwave Popcorn | Air-Popped Popcorn || Potato Chips | Baked Sweet Potato Fries |
Check Out This Amazing Guides
Processed foods are an integral part of the modern food landscape, but understanding their impact on health is crucial. By learning to differentiate between minimally processed and ultra-processed foods, reading labels carefully, and making informed choices, you can reduce your intake of unhealthy processed foods and improve your overall well-being. Focus on incorporating more whole, unprocessed foods into your diet, cooking at home, and staying informed about the latest research on nutrition. Prioritizing a balanced diet rich in whole foods will contribute to long-term health and vitality.
Affiliate Link Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products or services that I personally use and believe will be valuable to my readers.





