Fast Ketosis: Simple Tricks for Quick Results

Achieving ketosis, a metabolic state where your body burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates, can be a game-changer for weight loss, energy levels, and overall health. However, getting into ketosis quickly and efficiently can be challenging. This article provides seven easy-to-implement tricks to accelerate your journey into ketosis without unnecessary complications. We’ll cover dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and helpful supplements to guide you towards a fat-burning, energy-boosting state.
Understanding Ketosis: The Basics
Before diving into the tricks, let’s establish a fundamental understanding of ketosis. In simple terms, ketosis occurs when your body switches its primary fuel source from glucose (derived from carbohydrates) to ketones (produced from fat). This happens when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, forcing the body to tap into its fat reserves for energy.

- Glucose: The body’s preferred energy source, primarily derived from carbohydrates.
- Ketones: Produced by the liver from fat when glucose is scarce. These become the primary fuel source in ketosis.
- Ketogenesis: The process of producing ketones from fat.
- Keto-Adaptation: The period during which your body adjusts to using ketones for fuel.
The goal of these tricks is to deplete glycogen stores (stored glucose) and encourage your body to begin producing and utilizing ketones efficiently.
Trick 1: Slash Carbs Drastically
The cornerstone of ketosis is carbohydrate restriction. To induce ketosis quickly, you need to dramatically reduce your daily carb intake.
- Target Carb Intake: Aim for a maximum of 20-30 grams of net carbs per day. Net carbs are calculated by subtracting fiber from total carbohydrates (Total Carbs – Fiber = Net Carbs).
- Prioritize Low-Carb Foods: Focus on non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, etc.), healthy fats (avocados, olive oil, coconut oil), and protein sources (meat, poultry, fish).
- Eliminate High-Carb Culprits: Avoid grains (bread, pasta, rice), sugary drinks (soda, juice), starchy vegetables (potatoes, corn), fruits (especially high-sugar varieties), and processed foods.
- Read Labels Carefully: Hidden sugars and carbs lurk in many processed foods. Become a label-reading expert to ensure you stay within your carb limit.
Example: A sample low-carb meal might consist of grilled salmon with steamed broccoli drizzled with olive oil.
Why it Works: Reducing carbs forces your body to seek alternative fuel sources, initiating the process of ketogenesis. The more strictly you adhere to a low-carb diet, the faster you’ll deplete glycogen stores and enter ketosis.
Trick 2: Ramp Up Healthy Fats
Since you’re drastically reducing carbohydrates, you need to compensate with healthy fats. Fat becomes your primary energy source in ketosis.
- Increase Fat Intake: Aim for 70-80% of your daily calories from fat.
- Choose Healthy Fats: Prioritize sources like avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, MCT oil, nuts (almonds, macadamia), seeds (chia, flax), fatty fish (salmon, mackerel), and grass-fed butter.
- Avoid Unhealthy Fats: Limit processed vegetable oils (soybean, corn, canola), trans fats (found in many processed foods), and excessive amounts of saturated fat (though some saturated fat is acceptable).
- Track Your Macros: Use a food tracking app (MyFitnessPal, Carb Manager) to monitor your macronutrient intake (carbs, fat, protein) and ensure you’re hitting your targets.
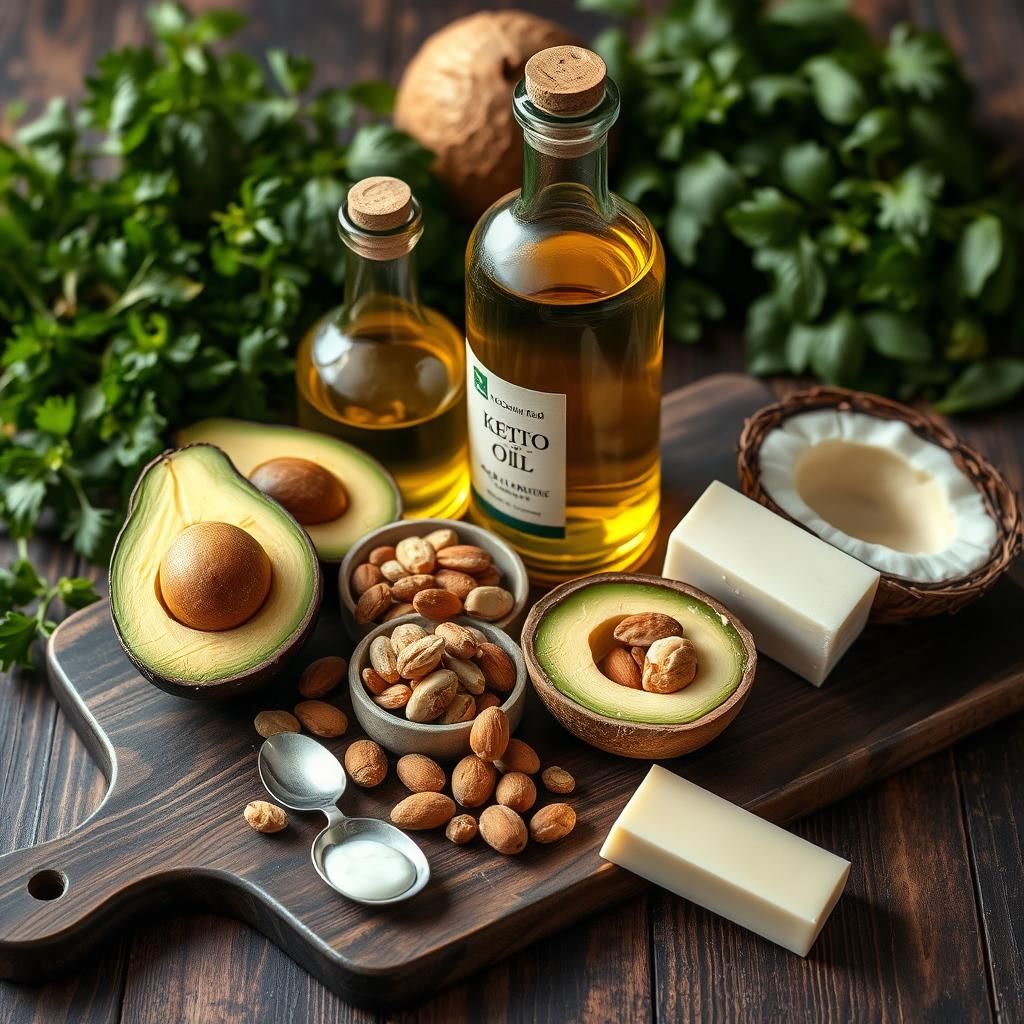

Example: Add a tablespoon of MCT oil to your coffee, snack on a handful of macadamia nuts, or drizzle olive oil over your salad.
Why it Works: Increasing fat intake provides the raw materials your liver needs to produce ketones. It also helps you feel satiated and prevents hunger pangs, making it easier to stick to the low-carb diet. Adequate fat intake is crucial for sustaining energy levels during keto-adaptation.
Trick 3: Moderate Protein Consumption
While protein is essential, excessive protein intake can hinder ketosis. The body can convert excess protein into glucose through a process called gluconeogenesis, potentially slowing down ketone production.
- Optimal Protein Intake: Aim for 20-25% of your daily calories from protein, or around 0.8-1.0 grams of protein per pound of lean body mass.
- Choose Quality Protein Sources: Opt for lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, and some dairy products (if tolerated).
- Avoid Overconsumption: While protein is important, don’t overdo it. Stick to the recommended intake to avoid hindering ketosis.
Example: A serving of grilled chicken breast or a couple of hard-boiled eggs provides a good source of protein without excessive carbohydrate content.
Why it Works: Moderating protein intake prevents the body from relying on gluconeogenesis for fuel, encouraging it to prioritize fat burning and ketone production. Striking the right balance of protein, fat, and carbs is crucial for efficient ketosis.
Trick 4: Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting (IF) can significantly accelerate the process of entering ketosis by depleting glycogen stores and promoting fat burning.
- Common IF Methods:
- 16/8 Method: Fast for 16 hours and eat all your meals within an 8-hour window.
- 5:2 Diet: Eat normally for five days of the week and restrict calorie intake (around 500-600 calories) on two non-consecutive days.
- Eat-Stop-Eat: Fast for 24 hours once or twice per week.
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to IF, begin with a shorter fasting window (e.g., 12 hours) and gradually increase it as your body adapts.
- Combine with Keto: Intermittent fasting is especially effective when combined with a ketogenic diet.

Example: Eat all your meals between 12 pm and 8 pm, fasting for the remaining 16 hours of the day.
Why it Works: During the fasting period, your body depletes glycogen stores and begins to tap into fat reserves for energy, accelerating ketone production. IF also improves insulin sensitivity, further enhancing fat burning.
Trick 5: Exercise Regularly
Physical activity, especially high-intensity exercise, can help deplete glycogen stores and promote fat burning.
- Types of Exercise:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods.
- Strength Training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands to build muscle mass.
- Cardio: Running, swimming, cycling, or brisk walking.
- Timing is Key: Consider exercising in a fasted state (before eating) to further deplete glycogen stores.
- Listen to Your Body: Start slowly and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts as your body adapts to ketosis.

Example: Engage in a 20-minute HIIT workout consisting of sprints, burpees, and push-ups.
Why it Works: Exercise, particularly HIIT, rapidly depletes glycogen stores, forcing your body to rely on fat for fuel and accelerating ketone production. Strength training helps build muscle mass, which increases your metabolic rate and enhances fat burning over time.
Trick 6: Supplement Wisely
Certain supplements can aid in the transition to ketosis and alleviate some of the initial side effects (the “keto flu”).
- MCT Oil: Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are rapidly absorbed and converted into ketones by the liver.
- Exogenous Ketones: Supplements containing ketones that you can ingest. They can help raise blood ketone levels quickly, but they are not a substitute for a ketogenic diet.
- Electrolytes: Sodium, potassium, and magnesium are often depleted during the initial stages of ketosis. Supplementing with electrolytes can help prevent dehydration, muscle cramps, and fatigue.
- Creatine: Can improve exercise performance and muscle strength, especially during the initial adaptation phase.
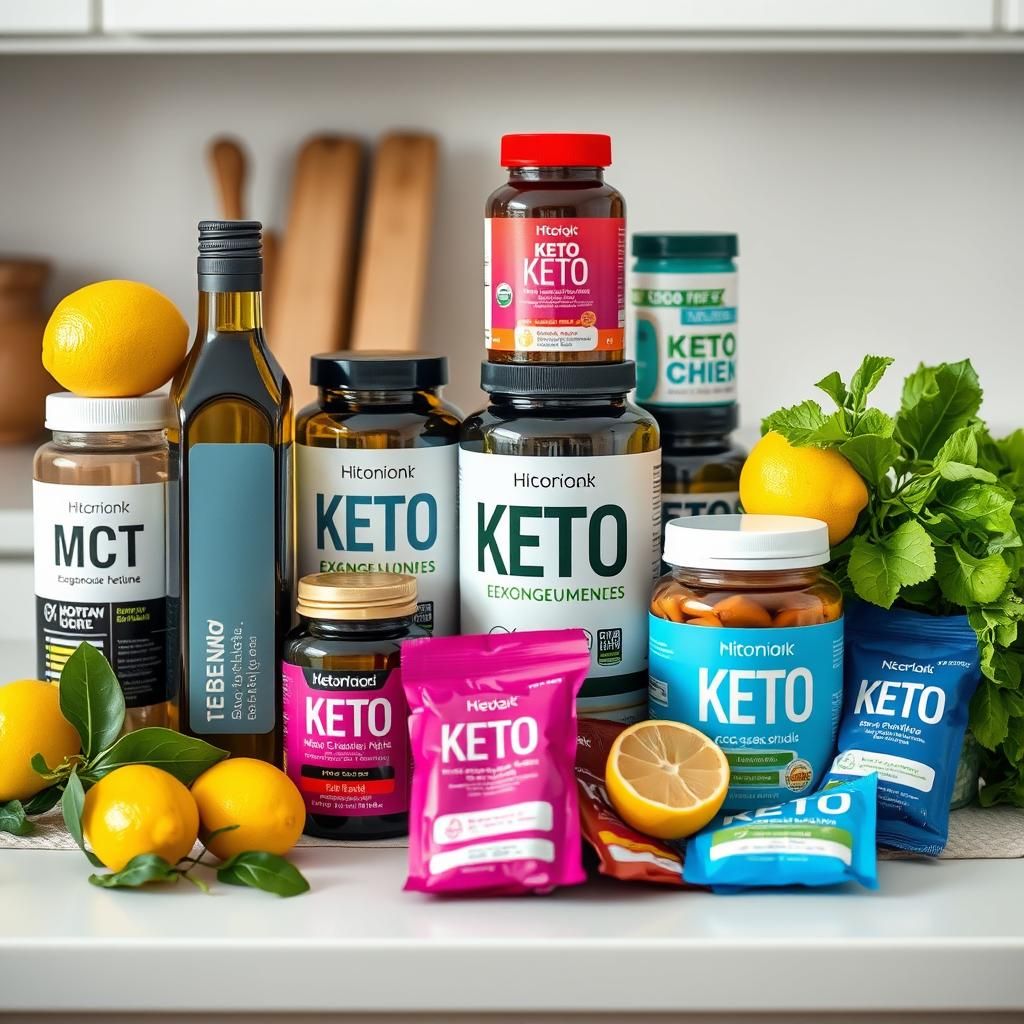

Dosage Recommendations (Consult with a Healthcare Professional):
- MCT Oil: Start with 1 teaspoon per day and gradually increase to 1-2 tablespoons.
- Exogenous Ketones: Follow the instructions on the product label.
- Electrolytes: Consider adding salt to your meals, drinking bone broth, or taking an electrolyte supplement.
- Creatine: 3-5 grams per day.
Why it Works: MCT oil provides a readily available source of ketones. Exogenous ketones can temporarily elevate ketone levels. Electrolytes help maintain fluid balance and prevent deficiencies. Creatine can boost energy and strength during workouts.
Trick 7: Monitor Ketone Levels
Tracking your ketone levels is essential for confirming that you’re actually in ketosis and for fine-tuning your diet and lifestyle.
- Methods for Measuring Ketones:
- Urine Strips: Convenient and inexpensive, but less accurate, especially over time.
- Blood Ketone Meter: More accurate than urine strips. Requires a small blood sample.
- Breath Ketone Analyzer: Measures acetone levels in your breath.
- Target Ketone Levels:
- Nutritional Ketosis: 0.5-3.0 mmol/L (measured with a blood ketone meter).
- Track Your Progress: Monitor your ketone levels regularly (e.g., once per day or every other day) and adjust your diet and lifestyle accordingly.
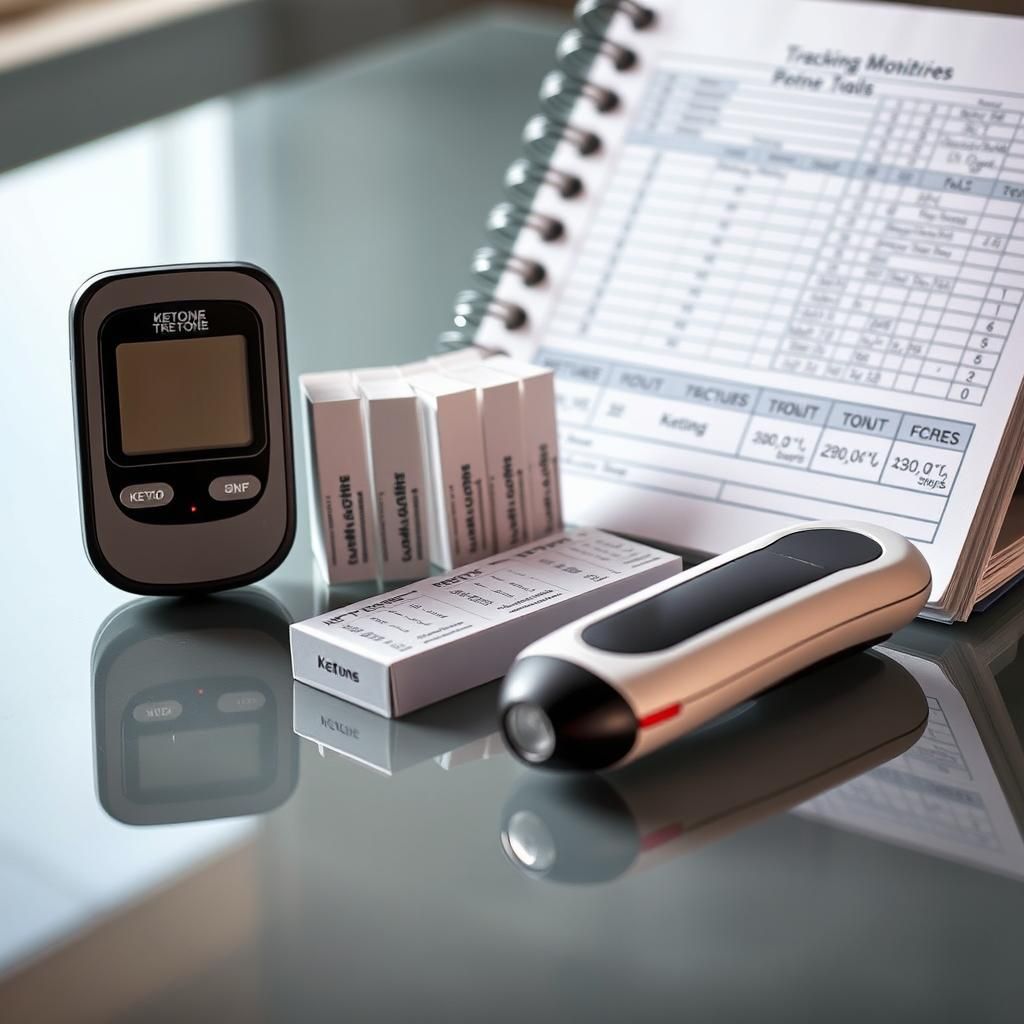

Example: Use a blood ketone meter to measure your ketone levels in the morning before eating.
Why it Works: Monitoring ketone levels provides objective feedback on whether you’re in ketosis and how your body is responding to the ketogenic diet and other interventions. This allows you to make informed adjustments to optimize your results.
Overcoming Common Challenges
The transition to ketosis can come with some challenges. Here’s how to address them:
- The “Keto Flu”: Flu-like symptoms (headache, fatigue, brain fog) that can occur during the initial stages of keto-adaptation. Combat the keto flu by staying hydrated, supplementing with electrolytes, and getting enough rest.
- Cravings: Cravings for carbs and sugary foods are common, especially in the beginning. Manage cravings by eating plenty of healthy fats, staying hydrated, and finding keto-friendly alternatives to your favorite foods.
- Digestive Issues: Some people experience constipation or diarrhea when starting a ketogenic diet. Increase your fiber intake (through non-starchy vegetables) and drink plenty of water to alleviate digestive issues.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Ensure you’re getting all the necessary vitamins and minerals by eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Consider taking a multivitamin if needed.

Long-Term Sustainability
While these tricks can help you get into ketosis quickly, it’s important to focus on long-term sustainability. The ketogenic diet is not a quick fix but rather a lifestyle change.
- Find Keto-Friendly Recipes You Enjoy: Experiment with different recipes and find meals that you find satisfying and sustainable.
- Plan Your Meals in Advance: Meal planning can help you stay on track and avoid impulsive choices.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to how you feel and adjust your diet and lifestyle as needed.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Experiment: Find what works best for you. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach to the ketogenic diet.
- Seek Professional Guidance: If you have any underlying health conditions, consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting a ketogenic diet.


Check Out These Resources!
By implementing these seven easy tricks – drastically cutting carbs, increasing healthy fats, moderating protein, incorporating intermittent fasting, exercising regularly, supplementing wisely, and monitoring ketone levels – you can accelerate your journey into ketosis and reap the benefits of fat burning, increased energy, and improved overall health. Remember to listen to your body, be patient with the adaptation process, and focus on long-term sustainability for lasting results. Ketosis is a powerful tool, but it requires commitment and informed choices. Embrace these tricks, and you’ll be well on your way to achieving your health and wellness goals.
Affiliate Link Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products or services that I personally use and believe will be valuable to my readers.






