Keto For Beginners: A Comprehensive Guide

The ketogenic diet, or keto, has exploded in popularity, lauded for its potential benefits in weight loss, blood sugar control, and even improved brain function. However, jumping into keto without a solid understanding of the fundamentals can lead to frustration, nutrient deficiencies, and ultimately, failure. This comprehensive guide provides 5 essential steps for beginners to successfully navigate the keto landscape.
1. Understand the Keto Basics
Before diving headfirst, grasp the underlying principles of the keto diet. Keto revolves around significantly reducing carbohydrate intake and replacing it with fat. This metabolic shift forces the body to enter a state called ketosis, where it starts burning fat for fuel instead of glucose (sugar). This process produces ketones, which become the body’s primary energy source.
Macronutrient Ratios
The typical keto macronutrient breakdown looks like this:
- 70-80% of calories from fat: This is the foundation of keto.
- 20-25% of calories from protein: Adequate protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass.
- 5-10% of calories from carbohydrates: This is the most restrictive aspect, typically limiting carb intake to under 50 grams per day, and for some, even less than 20 grams per day.
It’s vital to understand that these are guidelines, and individual needs may vary based on activity level, metabolism, and other factors. Using a keto calculator (readily available online) can help you determine your specific macronutrient targets.
The Science Behind Ketosis
Ketosis is a natural metabolic state. When glucose is scarce, the liver breaks down fat into fatty acids and ketones. These ketones, primarily acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), and acetone, become an alternative fuel source for the brain, muscles, and other tissues.
- Acetoacetate: The first ketone body produced.
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB): The most abundant ketone body in the blood.
- Acetone: A ketone body produced in smaller amounts, often exhaled through the breath.
Ketosis is often measured by testing ketone levels in the blood, urine, or breath. Blood ketone meters are the most accurate, while urine strips are the least reliable.
Busting Common Keto Myths
- Myth: Keto is a high-protein diet. Keto is primarily a high-fat diet, with moderate protein intake. Excessive protein can be converted to glucose, hindering ketosis.
- Myth: You can eat unlimited fat on keto. While fat is the primary fuel source, calorie control still matters for weight loss.
- Myth: Keto is unhealthy long-term. Research on the long-term effects of keto is ongoing. However, a well-formulated keto diet, rich in nutrient-dense foods, can be sustainable for many individuals. Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential.
2. Plan Your Keto-Friendly Meals
Successful keto implementation hinges on meticulous meal planning. This involves identifying keto-friendly foods and crafting meal plans that meet your macronutrient goals.
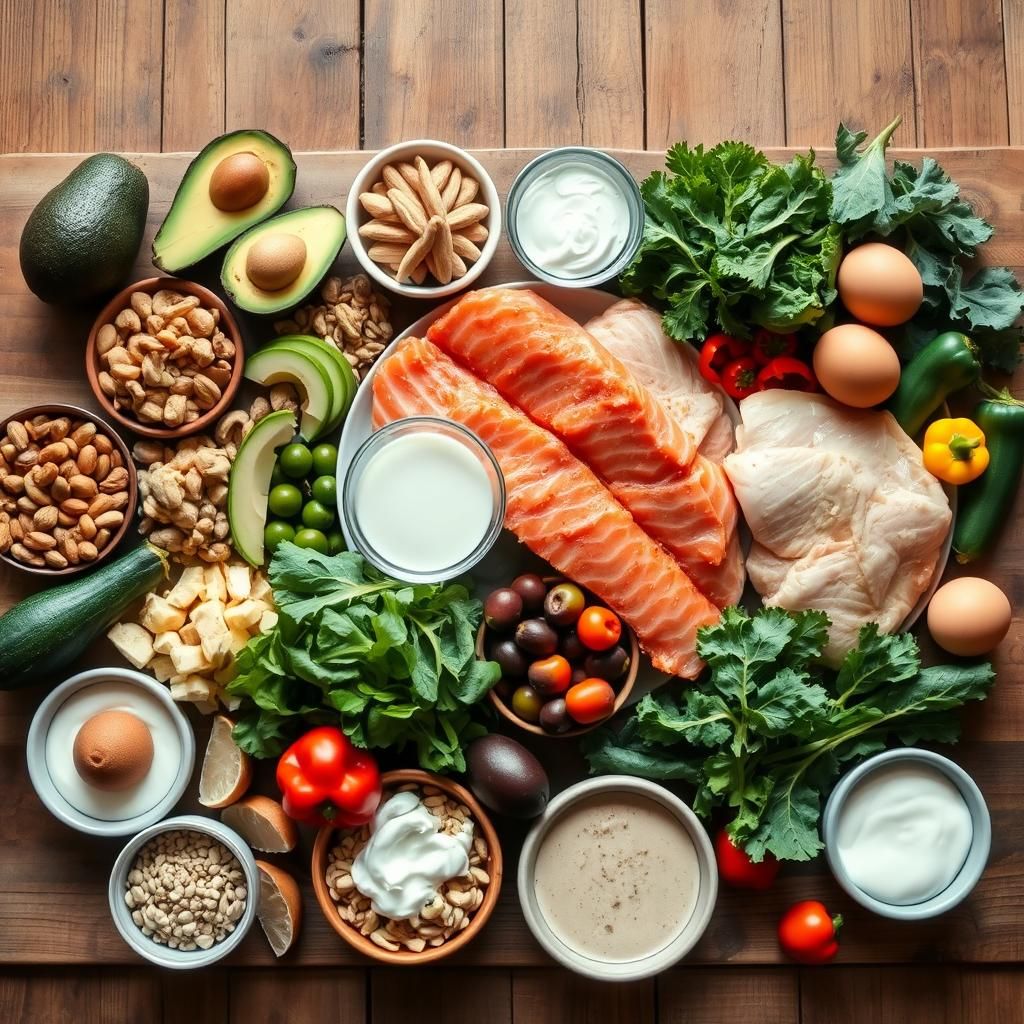

Keto-Friendly Food List
- Healthy Fats: Avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, MCT oil, nuts and seeds (macadamia, almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds), fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), full-fat dairy (cheese, heavy cream, Greek yogurt in moderation).
- Protein Sources: Meat (beef, pork, chicken, lamb), poultry, fish, eggs, tofu, tempeh (in moderation).
- Low-Carb Vegetables: Leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce), broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, zucchini, bell peppers, avocados.
- Dairy (Full Fat, Limited): Heavy Cream, Cream Cheese, Hard Cheeses
- Berries (Limited): Blueberries, raspberries, strawberries (in small portions due to their carbohydrate content).
Foods to Avoid on Keto
- Grains: Wheat, rice, corn, oats, barley.
- Sugary Foods: Candy, soda, juice, pastries, ice cream.
- Starchy Vegetables: Potatoes, sweet potatoes, corn, peas.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, chickpeas (some exceptions may apply in small quantities).
- Most Fruits: Bananas, apples, oranges, grapes (berries are generally acceptable in moderation).
- Processed Foods: Many processed foods are high in carbs and unhealthy fats.
- Low-Fat or Diet Foods: Often high in added sugars to compensate for the lack of fat.
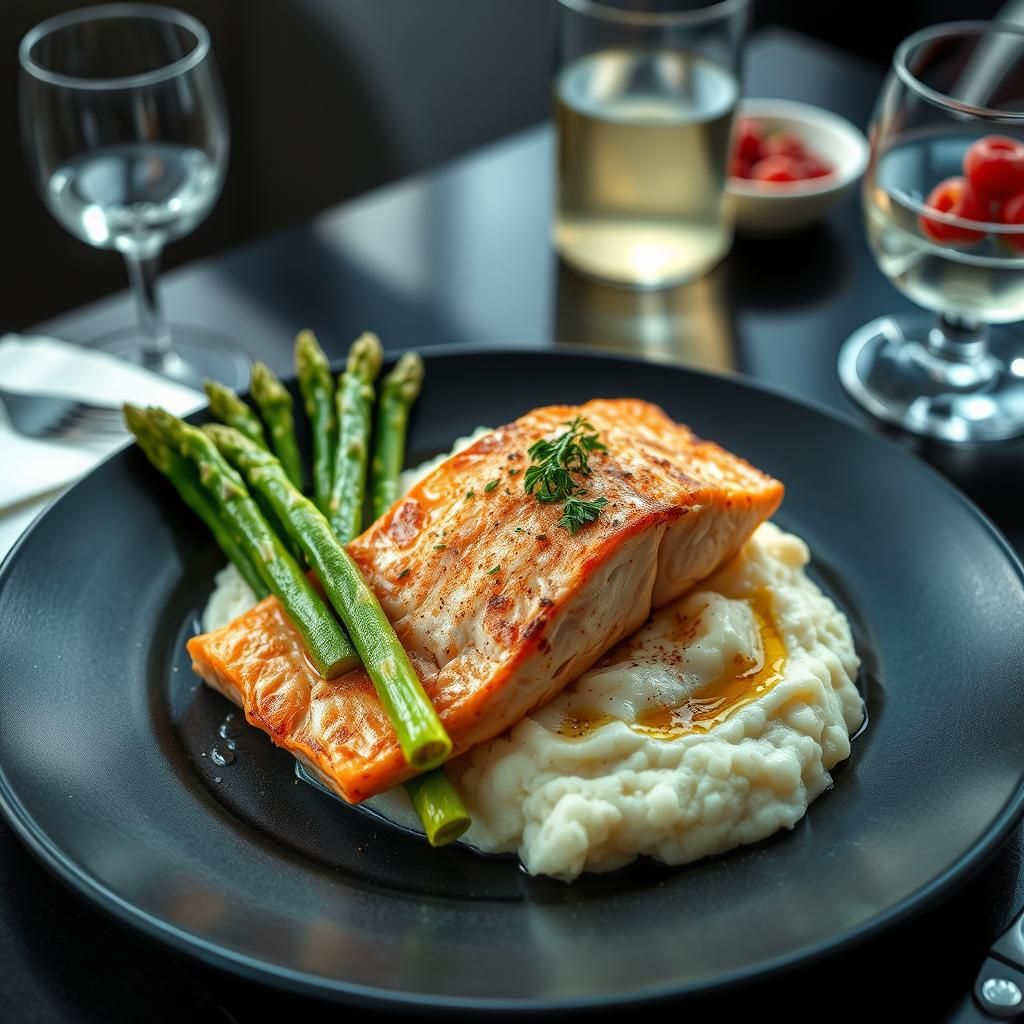
Sample Keto Meal Plan (One Day)
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with cheese and avocado.
- Lunch: Salad with grilled chicken, olive oil dressing, and avocado.
- Dinner: Salmon baked with asparagus and a side of cauliflower mash.
- Snacks: Macadamia nuts, cheese slices, or a small handful of berries.

Meal Prep Strategies
- Cook in bulk: Prepare large batches of keto-friendly meals on weekends to save time during the week.
- Pre-portion snacks: Divide nuts, cheese, and other snacks into individual servings to avoid overeating.
- Use meal planning apps: Several apps can help you track your macronutrients and plan keto-friendly meals.

3. Manage the Keto Flu and Electrolyte Imbalance
The “keto flu” is a common side effect experienced during the initial stages of the keto diet as the body adapts to using fat for fuel. It is not the actual flu, but rather a constellation of symptoms. Electrolyte imbalances are also common as the body sheds water and electrolytes when carbohydrate intake is restricted.
Symptoms of the Keto Flu
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Brain fog
- Irritability
- Muscle cramps
- Constipation
- Dizziness
Causes of the Keto Flu
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Reduced insulin levels (due to low carb intake) lead to increased sodium and potassium excretion.
- Dehydration: The kidneys excrete more water in the initial stages of ketosis.
- Glucose Withdrawal: The body’s initial reaction to being deprived of its primary energy source.

Strategies to Manage the Keto Flu and Electrolyte Imbalance
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water, ideally with added electrolytes.
- Increase Electrolyte Intake:
- Sodium: Add salt to your meals and snacks. Consider drinking bone broth.
- Potassium: Eat potassium-rich keto-friendly foods like avocados, spinach, and mushrooms. Consider a potassium supplement (consult with a healthcare professional).
- Magnesium: Take a magnesium supplement (glycinate or citrate are good options). Magnesium deficiency is common.
- Gradual Carb Reduction: Instead of drastically cutting carbs overnight, gradually reduce your intake over a week or two.
- Increase Fat Intake: Ensure you’re consuming enough healthy fats to fuel your body.
- Light Exercise: Avoid strenuous activity during the initial stages.
- Bone Broth: An excellent source of electrolytes and minerals.
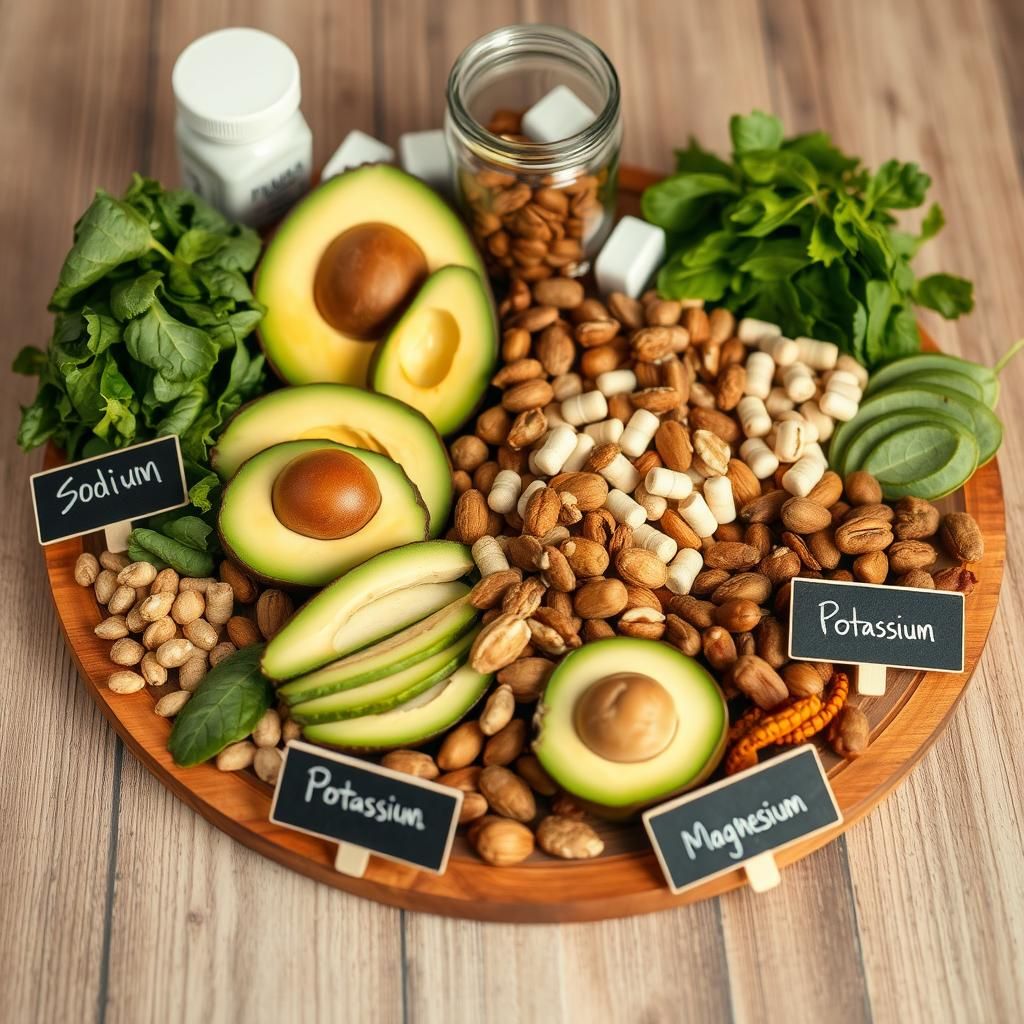

Importance of Electrolyte Supplementation
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge and are essential for various bodily functions, including muscle contraction, nerve function, and fluid balance. During keto, the body excretes more electrolytes, making supplementation crucial.
- Sodium: Essential for fluid balance and nerve function.
- Potassium: Vital for muscle contractions and heart health.
- Magnesium: Involved in hundreds of enzymatic reactions and crucial for muscle relaxation.
4. Track Your Progress and Adjust Accordingly
Monitoring your progress is essential for determining if the keto diet is working for you and making necessary adjustments.

Methods for Tracking Progress
- Weight: Weigh yourself regularly (but not obsessively). Focus on overall trends rather than daily fluctuations.
- Measurements: Track your waist, hips, and other body measurements.
- Ketone Levels: Use blood, urine, or breath ketone meters to measure ketone levels. Blood meters are the most accurate, while urine strips are less reliable.
- Food Journal: Record everything you eat to track your macronutrient intake and identify potential problem areas.
- Energy Levels: Monitor your energy levels throughout the day. Improved energy is a positive sign of keto adaptation.
- Appetite: Notice changes in your appetite. Keto often suppresses hunger.
- Sleep Quality: Track your sleep quality. Keto can improve sleep for some individuals.
- Blood Glucose Levels (If Applicable): If you have diabetes or insulin resistance, monitor your blood glucose levels regularly.
Interpreting Your Results
- Weight Loss: Gradual weight loss is a positive sign. Aim for 1-2 pounds per week.
- Ketone Levels: Aim for ketone levels between 0.5 and 3.0 mmol/L (for blood meters).
- Macronutrient Tracking: Ensure you’re meeting your macronutrient targets. Adjust your meal plan as needed.
- Energy Levels: Improved energy levels indicate successful keto adaptation.
- Blood Glucose Levels: If you have diabetes, monitor your blood glucose levels closely and adjust your medication as needed (under the guidance of your healthcare provider).
Adjusting Your Approach
- If You’re Not Losing Weight: Re-evaluate your calorie intake, track your food intake meticulously, and ensure you’re in a calorie deficit. Also, check ketone levels to make sure you are in ketosis.
- If You’re Experiencing Low Energy: Increase your fat intake, ensure you’re getting enough electrolytes, and consider adding MCT oil to your diet.
- If You’re Having Digestive Issues: Increase your fiber intake through low-carb vegetables and consider a probiotic supplement.
- If You’re Not in Ketosis: Reduce your carbohydrate intake further, track your food intake meticulously, and eliminate hidden sources of carbs.
5. Focus on Nutrient Density and Long-Term Sustainability
The long-term success of the keto diet depends on prioritizing nutrient-dense foods and making sustainable lifestyle choices.

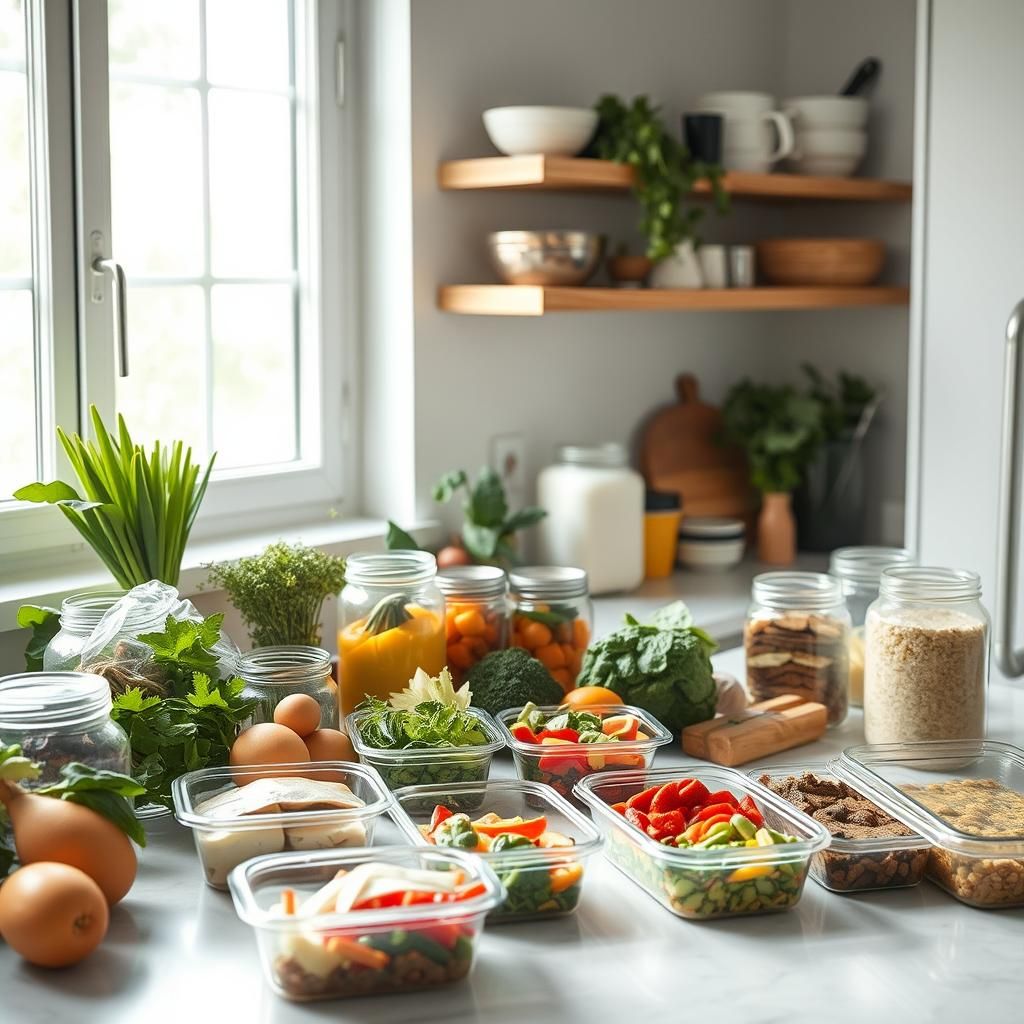
Prioritizing Nutrient-Dense Foods
- Choose Whole, Unprocessed Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like meat, fish, eggs, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Variety is Key: Consume a wide variety of keto-friendly vegetables to ensure you’re getting a broad range of nutrients.
- Don’t Neglect Micronutrients: Pay attention to your intake of vitamins and minerals. Consider a multivitamin if needed.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies on Keto and How to Address Them
- Electrolytes (Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium): Supplement as needed and consume electrolyte-rich foods.
- Fiber: Eat plenty of low-carb vegetables. Consider psyllium husk or chia seeds.
- Vitamin D: Supplement with vitamin D, especially during the winter months.
- Calcium: Consume full-fat dairy (in moderation) or supplement with calcium.
- Iron: Eat iron-rich foods like red meat, spinach, and liver.
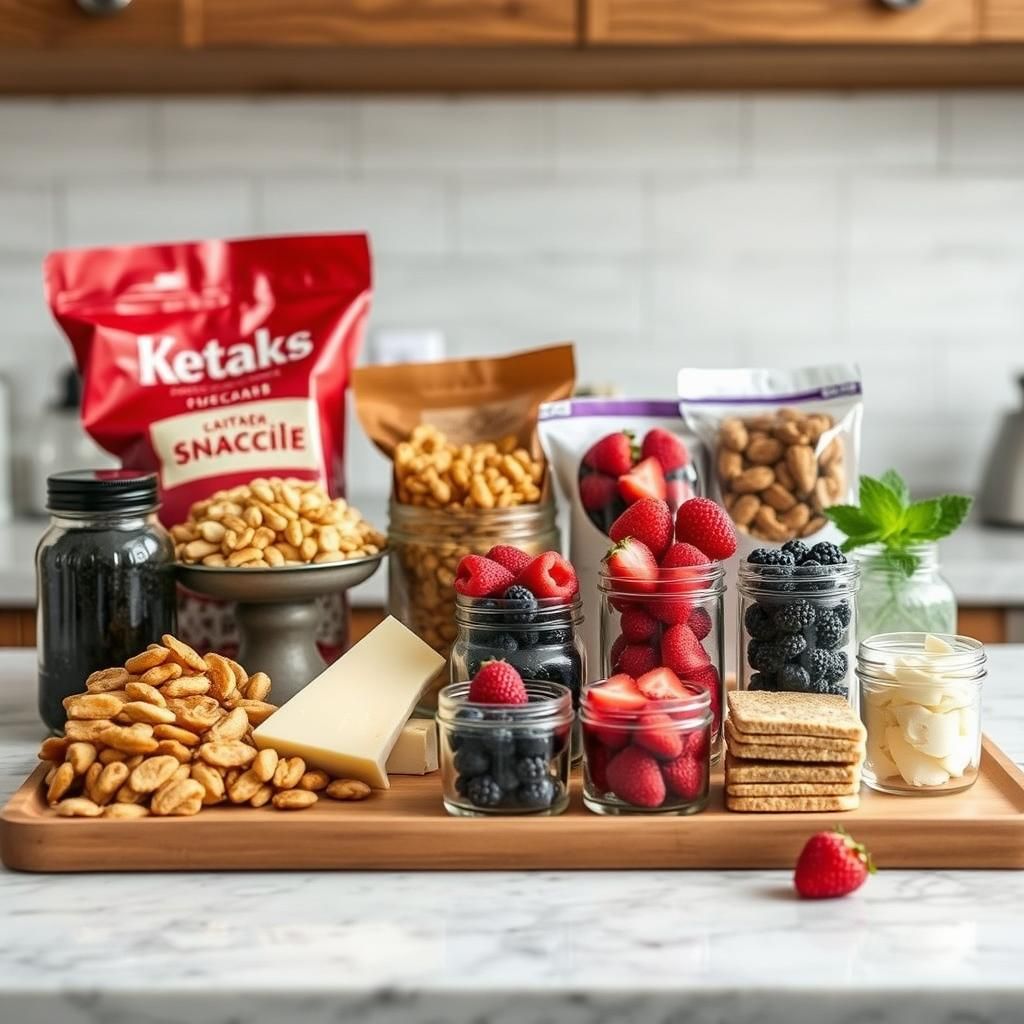


Making Keto Sustainable Long-Term
- Find Keto-Friendly Alternatives: Replace your favorite high-carb foods with keto-friendly alternatives.
- Plan for Social Situations: Have a strategy for eating out or attending social events.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust your diet accordingly.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Experiment: Find what works best for you and your individual needs.
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: Talk to your doctor or a registered dietitian before starting the keto diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Keto Variations: Cyclical and Targeted Keto
- Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD): Involves periods of keto followed by periods of higher carbohydrate intake. This may be suitable for athletes or individuals who find strict keto difficult to maintain long-term.
- Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD): Allows for carbohydrate consumption around workouts to fuel performance.
Embarking on a ketogenic diet can be a transformative journey, but it requires education, planning, and consistency. By understanding the fundamentals of keto, planning your meals, managing the keto flu, tracking your progress, and prioritizing nutrient density, you can increase your chances of success and reap the potential benefits of this popular diet. Remember to listen to your body, adapt your approach as needed, and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance. The road to keto success is paved with knowledge, patience, and a commitment to a healthier lifestyle.
Check Out These Helpful Resources!
Affiliate Link Disclosure: Some of the links in this post are affiliate links. This means that if you click on the link and make a purchase, I may receive a small commission at no extra cost to you. I only recommend products or services that I personally use and believe will be valuable to my readers.